Tutorial: Data transformation
- Preparation
- Implementation
Idea
Make a project that calculates how Canadian a string is. As an added bonus, it will determine the emotion of the string based on how eh’s are used.
Requirements
Use:
- our own components
- other peoples components (other noflo libraries components)
- can use fbp
- graphs
- subgraphs
- tests (use fbp-spec and mocha tests to show both options)
- debugging
Planning
- To determine how Canadian something is, we want to check words inside of the string.
- ~ If it is easily possible, figure out how far words are from each other
- ~ and their location inside of the string (ie, at the very end, beginning, near the end.)
- Check spelling of words, Canadan vs elsewhere. Canadian spelling first, then UK, then American.
- Check the emotion of the word eh using symbols and letter case (ie, eh, Eh, EH, EH?, eh?!)
- The output should have the Emotion, and the Canadian Score.
Researching
Word Weight
Search Google for a library that may be able to help us with dealing with word weights, singularize, and pluralize words. js library determine weight of words NaturalNode looks promising
Spelling
Search Google for the spelling differences Canadian vs uk vs usa spelling
perfect Canadian, British and American Spelling This is data on a table though with no apparent api, so we should get it into usable data (json). get table as json table to json table to json jquery
Pseudo code
[How Canadian]
INPUT=CONTENT(string)
INPUT=WORDS(array) # words to use as weights
INPUT=SPELLING(array)
OUTPUT=EMOTION(string)
OUTPUT=SCORE(number)
# if we wanted to swap out emotion to calculate emoji insteadof _eh_ for example,
# we can easily just replace this box. the same goes for any noflo box.
[Emotion]
INPUT=CONTENT(string)
OUTPUT=EMOTION(string)
[Find Ehs]
# if it has no _eh_, emotion is flat
# could also separate to collect and doing each and then sending another stream
# and putting those back together as a score and using add
# collects stream, determines emotion of each
[Determine Emotion]
[WordScore]
OUTPUT=SCORE(number)
INPUT=LIST(array) # control port, because we want to use one for each input
INPUT=CONTENT(STRING)
# since these both calculate score, one positive, one negative,
# they can be separate instances of the same component
[CanadianScore] # LIST would use WORDS
[SpellingScore] # LIST would use SPELLING
# output of CanadianScore & SpellingScore should be added together to get result
# score from here is the SCORE
[noflo/Math/Add]
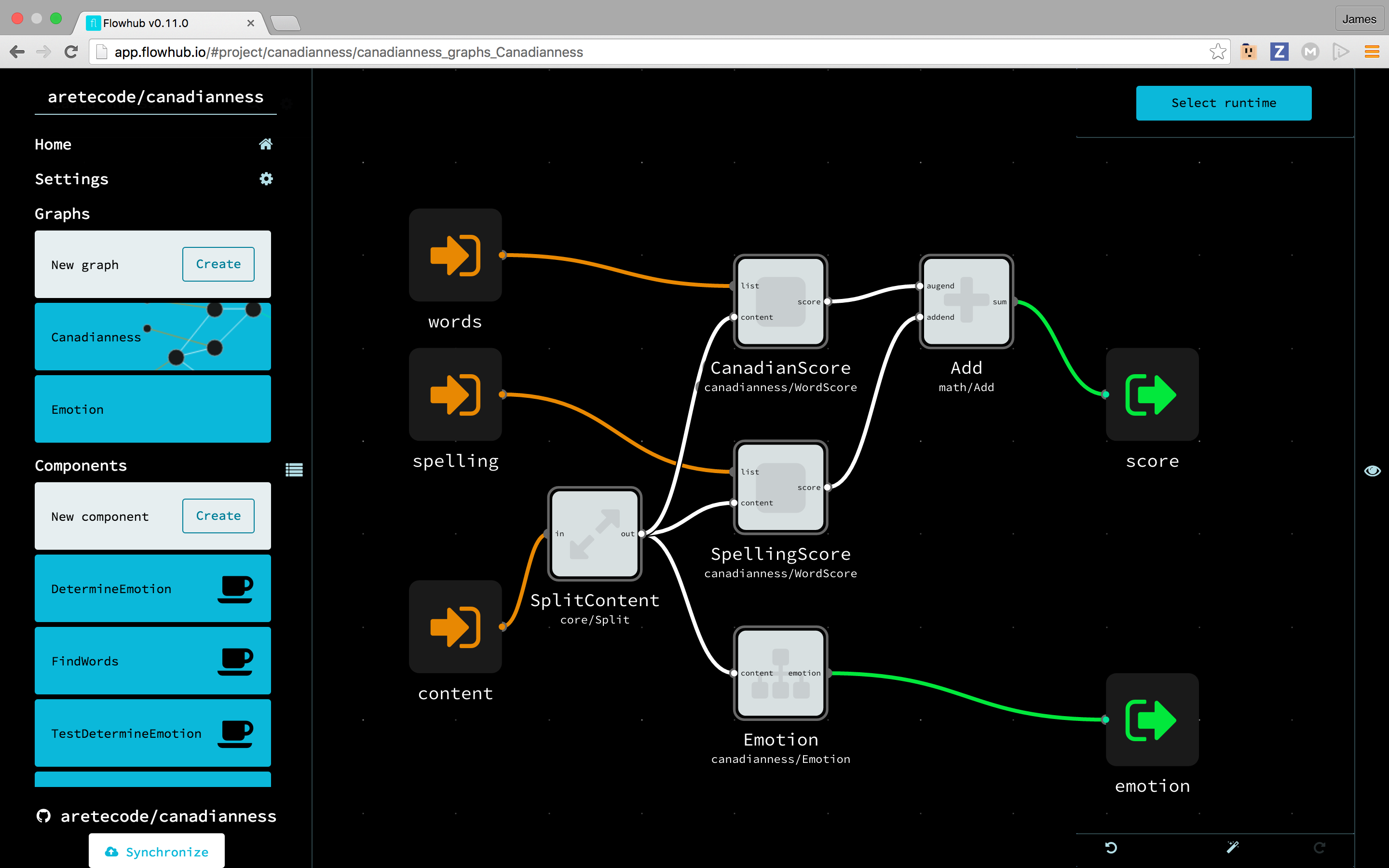
Overall architecture
Canadianness
Real graph implementation of pseudo code:
# (string)
INPORT=SplitContent.IN:CONTENT
# (array)
INPORT=SpellingScore.LIST:SPELLING
# (array)
INPORT=CanadianScore.LIST:WORDS
# (string)
OUTPORT=Emotion.EMOTION:EMOTION
# (int)
OUTPORT=Add.SUM:SCORE
# [core/Split](https://github.com/noflo/noflo-core/blob/master/components/Split.coffee) takes the input
# and sends it to each of the [sockets](http://noflojs.org/api/InternalSocket/) attached to the outport
# ----
# Emotion is subgraph
SplitContent(core/Split) OUT -> CONTENT Emotion(canadianness/Emotion)
SplitContent OUT -> CONTENT SpellingScore(canadianness/WordScore)
SplitContent OUT -> CONTENT CanadianScore(canadianness/WordScore)
SpellingScore SCORE -> ADDEND Add(math/Add)
CanadianScore SCORE -> AUGEND Add
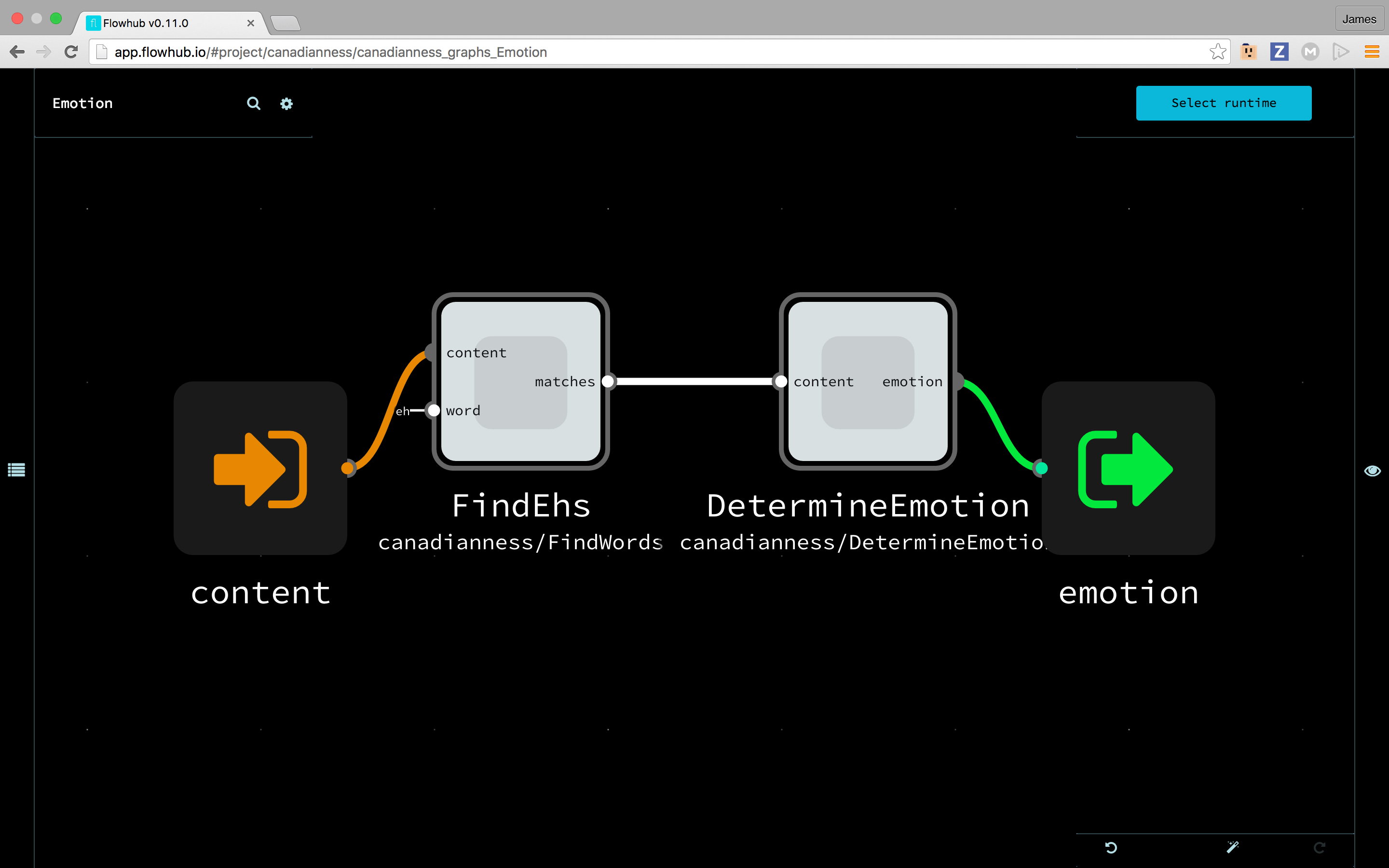
Emotion
This can be its own graph loaded inside of the main graph as a subgraph so the whole operation can be represented as a box:
# (string)
INPORT=FINDEHS.CONTENT:CONTENT
# (string)
OUTPORT=DetermineEmotion.EMOTION:EMOTION
FindEhs(FindEhs) MATCHES -> CONTENT DetermineEmotion(DetermineEmotion)
Writing tests
First in line for testing, we have fbp-spec
Just add a fbpspec.js file in /spec directory
Important to note, you cannot send brackets or do any sort of special operations using fbp-spec. To get around that, you will can write components exclusively for testing, and fbp graphs as fixtures.
The command we use for noflo, and the flags can be found at noflo-nodejs flags
const fbpspec = require('fbp-spec');
const nodeRuntime = {
label: "NoFlo node.js",
description: "",
type: "noflo",
protocol: "websocket",
secret: 'notasecret',
address: "ws://localhost:3333",
id: "7807f4d8-63e0-4a89-a577-2770c14f8106",
command: './node_modules/.bin/noflo-nodejs --catch-exceptions=false --secret notasecret --port=3333 --host=localhost --register=false --capture-output=true'
};
fbpspec.mocha.run(nodeRuntime, './spec', {
fixturetimeout: 10000,
starttimeout: 10000
});
Then, for each test, just add a yaml file in the /spec directory, each yaml file in /spec is loaded by the fbp-spec.
topic: "canadianness/FindWords"
name: "Find words fbpspec"
cases:
-
name: 'content eh'
assertion: 'should be find one `eh`'
inputs:
word: 'eh'
surrounding: false
content: 'eh'
expect:
matches:
equals: 'eh'
Implement components
DetermineEmotion
Import libraries
const noflo = require('noflo');Useful functions
Function to calculate most common value (the mode
function findMode(array) {
const frequency = {};
let maxFrequency = 0;
let result;
array.forEach((v) => {
frequency[v] = (frequency[v] || 0) + 1;
if (frequency[v] > maxFrequency) {
maxFrequency = frequency[v];
result = v;
}
});
return result;
}Component declaration
Define the input and output ports, and describe their function
exports.getComponent = () => {
const c = new noflo.Component({
description: 'Find all of the instances of `word` in `content` and send them out in a stream',
inPorts: {
content: {
datatype: 'string',
description: 'the content which we look for the word in',
required: true,
},
},
outPorts: {
emotion: {
datatype: 'string',
description: 'the emotion based the content in ehs',
required: true,
},
error: {
datatype: 'object',
},
},
});Since we want to work with a full stream, we disable bracket forwarding
c.forwardBrackets = {};Processing function
c.process((input, output) => {Receiving input
We expect a stream Will also accept a single (non-bracketed) input packet, returned as a stream of length 1
if (!input.hasStream('content')) { return; }The output will be a single packet (not a stream),
hence we drop the openBracket and closeBracket
and extract the data payload from the IP objects
const contents = input.getStream('content').filter((ip) => ip.type === 'data').map((ip) => ip.data);Component business logic
First find which emotions are present, then calculate which one is most common. This could alternatively be split into two dedicate components.
to hold the emotions found
const matches = [];the emotions we will use
const emotions = {
joy: ['eh!'],
neutral: ['eh'],
amusement: ['eh?', 'Eh?', 'Eh??'],
fear: ['eH??', 'eh??'],
surprise: ['eh !?', 'EH!?'],
anticipation: ['eh?!'],
excitment: ['EH!', 'eH!'],
sadness: ['...eh', '...eh...', '..eh', 'eh..', '..eh..'],
anger: ['EH!?', 'EH?'],
};go through our content and our emotions
then add them to our matches
contents.forEach((content) => {
Object.keys(emotions).forEach((emotion) => {
const data = emotions[emotion];
if (data.indexOf(content) !== -1) {
matches.push(emotion);
}
});
});if we didn’t get any emotions, it default to ‘neutral’
let mode;
if (matches.length === 0) {
mode = 'neutral';if we did, we need to find the emotion that was the most common
} else {
mode = findMode(matches);
}Send output
Also signals completion by using sendDone()
output.sendDone({
emotion: mode,
});
});
return c;
};FindWords
Import libraries
const noflo = require('noflo');Helper functions
Not NoFlo or even component-logic-specific, so nice to keep them separate
Return all RegExp matches on a string
function matchAll(string, regexp) {
const matches = [];
string.replace(regexp, (...rest) => {
const arr = rest.slice(0);
const extras = arr.splice(-2);
[arr.index, arr.input] = extras;
matches.push(arr);
});
if (matches.length) {
return matches;
}
return [];
}Extract the actual data of the match result
function actualMatches(matches) {because we want to send out an empty array if there are no matches
if (matches.length === 0) { return [[]]; }
return matches.map((match) => match[0]);
}Component declaration
exports.getComponent = () => {
const c = new noflo.Component({
description: 'Find all of the instances of `word` in `content` and send them out in a stream',
inPorts: {
content: {
datatype: 'string',
description: 'the content which we look for a word in',
required: true,
},
word: {
datatype: 'string', // could be array|string, which would be `all`
description: 'the word we are looking for instances of',
control: true,
required: true,
},
surrounding: { // could use a regex but this is a specific case
datatype: 'boolean',
description: 'whether to get surrounding characters, symbols before and after until space',
default: false, // if nothing is sent to it, this is the default when `get`ting from it
control: true,
},
},
outPorts: {
matches: {
datatype: 'string',
description: 'the resulting findings as a stream of data packets',
required: true,
},
},
});Processing function
To preserve streams, forward brackets from the primary inport content to the output.
c.forwardBrackets = {
content: ['matches'],
};
c.process((input, output) => {Receiving input data
We need both a word, and content to start processing
Since word is a control port, the latest value is kept, no need to continiously send
if (!input.hasData('word', 'content')) { return; }const [word, content] = input.getData(‘word’, ‘content’);
const content = input.getData('content');Component business logic
since we are sending out multiple data IPs
we want to wrap them in brackets
TODO: make exception safe
output.send({
matches: new noflo.IP('openBracket', content),
});do our word processing
const r = /([.?!]*eh[.?!]*)/gi;
let matches = matchAll(content, r);
matches = actualMatches(matches);Sending output
for each of our matches, send them out
matches.forEach((match) => {if you just send content, it will automatically put it in a data ip
so this is the same as output.send matches: new noflo.IP 'data', match
output.send({
matches: match,
});
});this is the same as doing output.send and then output.done
output.sendDone({
matches: new noflo.IP('closeBracket', content),
});
});
return c;
};WordScore
Import libraries
const noflo = require('noflo');
const natural = require('natural');
const tokenizer = new natural.WordTokenizer();Component declaration
exports.getComponent = () => {
const c = new noflo.Component({
description: 'Find how the input words compare against the list of weighted words',
inPorts: {
list: {
datatype: 'array',
description: 'list of words we will use with the list of content',
control: true,
required: true,
},
content: {
datatype: 'string',
description: 'the content which we will determine the score of',
required: true,
},
},
outPorts: {
score: {
datatype: 'number',
description: 'the resulting number of comparing the content with the list',
required: true,
},
},
});Processing function
To preserve streams, forward brackets from the primary inport to the output.
c.forwardBrackets = {};
c.process((input, output) => {Receive input
let scoringFunction;
if (!input.hasStream('content')) { return; }
if (!input.hasData('list')) { return; }
let content = input.getStream('content').filter((ip) => ip.type === 'data').map((ip) => ip.data);
const list = input.getData('list');there can be multiple pieces of content
content = content.join('\n');Component business logic
our base score we will send out
let score = 0;splits content into an array of words
const tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(content);if the list has the word in it, return the score otherwise, 0 points
const wordScore = (word) => {
if (list[word] != null) {
return list[word];
}
return 0;
};go through each of the comparisons in the list if it is Canadian: 1, American: -1, British: .5, None: 0
const spellingScore = (word) => {
let value = 0;
list.forEach((comparison) => {
if (comparison.American.indexOf(word) !== -1) {
value = -1;
return;
}
if (comparison.Canadian.indexOf(word) !== -1) {
value = 1;
return;
}
if (comparison.British.indexOf(word) !== -1) {
value = 0.5;
}
});
return value;
};if it has this, it is a spelling list
if ((list[0] != null ? list[0].Canadian : undefined) != null) {
scoringFunction = spellingScore;otherwise it is an object list of words with scores
} else {
scoringFunction = wordScore;
}use this to singularize and pluralize each word
const nounInflector = new natural.NounInflector();go through each item in contents
tokens.forEach((data) => {
const plural = nounInflector.pluralize(data);
const singular = nounInflector.singularize(data);if it is already plural or singular do not use it
if (plural !== data) {
score += scoringFunction(plural);
}
if (singular !== data) {
score += scoringFunction(singular);
}
score += scoringFunction(data);
});Send output
output.sendDone({
score,
});
});
return c;
};Providing a JavaScript API
If we want to make the NoFlo project also available to regular JavaScript users, it is possible to utilize the NoFlo embedding API to produce a regular Node.js style function.
const noflo = require('noflo');
const defaultSpellingData = require('./spellingdata.json');
const defaultWords = {
eh: 11,
'eh!': 11,
};Produce the JavaScript entry point
function canadianness(contentData, options, callback) {Normalize options
const spellingData = options.spelling || defaultSpellingData;
const wordsData = options.words || defaultWords;Convert options and input to a set of NoFlo packets to be sent
const inputs = {
words: wordsData,
spelling: spellingData,
content: contentData,
};Produce a NoFlo.asCallback wrapped function to execute our graph
const componentName = 'canadianness/Canadianness';
const wrapperFunction = noflo.asCallback(componentName, {
baseDir: __dirname,
});Run the graph with inputs and call callback
wrapperFunction(inputs, callback);
}Expose function as public API
module.exports = canadianness;